Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic and debilitating condition that affects the limbs, causing severe pain, swelling, and other distressing symptoms. Diagnosing CRPS can be a challenging endeavor due to its complex nature and varying symptoms. To aid in the accurate diagnosis of this condition, a set of diagnostic guidelines known as the Budapest Criteria was developed.
Understanding CRPS
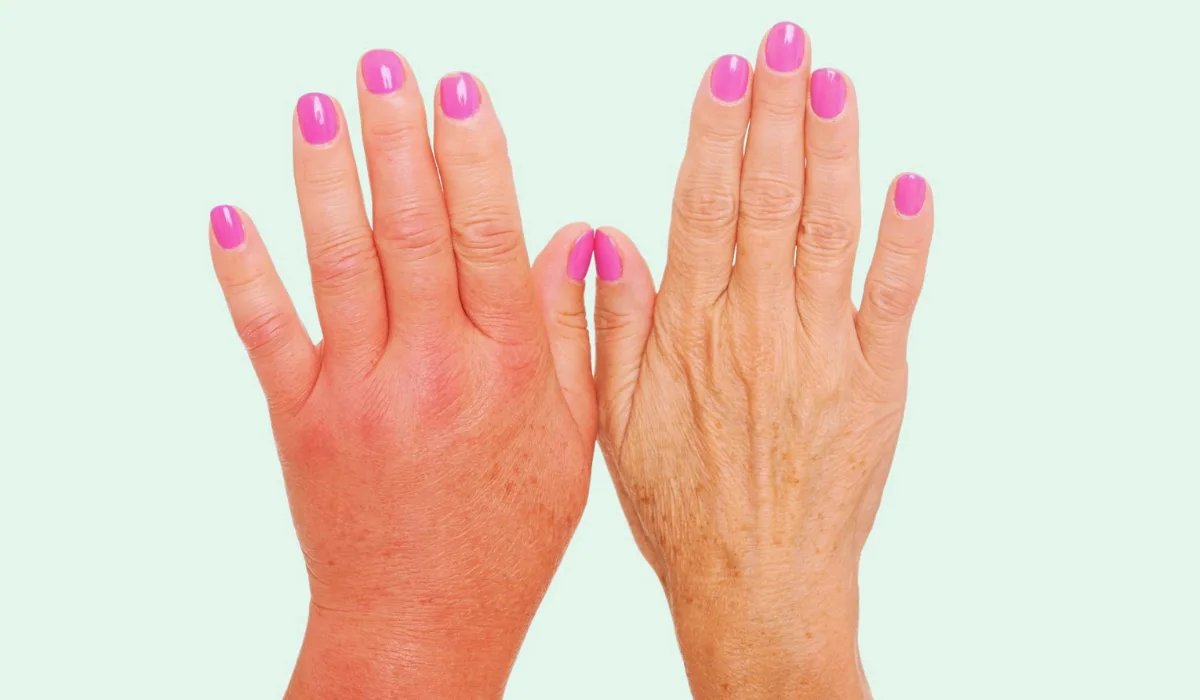
CRPS, formerly known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD), is a chronic pain condition that typically affects one or more limbs. It is characterized by severe, persistent pain that is disproportionate to the initial injury or event that triggered it. The pain is often described as burning, throbbing, or shooting, and it can be accompanied by changes in skin color, temperature, and swelling.

The prevalence of CRPS is estimated to be around 20 cases per 100,000 people annually, with women being affected more frequently than men. The condition can occur at any age, but it is more common in individuals between the ages of 40 and 60.
The primary symptoms of CRPS include:
- Severe, constant pain in the affected limb(s)
- Swelling and changes in skin temperature (either warmer or cooler than the unaffected limb)
- Changes in skin color (often reddish or bluish)
- Abnormal sweating or excessive sweating in the affected limb(s)
- Limited mobility and decreased range of motion
CRPS can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life, affecting their ability to perform daily activities, work, and engage in social interactions. Early detection and treatment are very important for controlling the condition and stopping it from getting worse.
The Budapest Criteria
The Budapest Criteria were developed in 2007 by a group of international experts to provide a standardized diagnostic framework for CRPS. These criteria aim to promote consistent and accurate diagnosis of the condition, which is essential for appropriate treatment and management.
The Budapest Criteria were developed through a process of consensus among experts in the field, taking into account the latest research and clinical evidence. They are widely recognized and utilized by healthcare professionals worldwide.
The Budapest Criteria consist of four main diagnostic categories: sensory, vasomotor, sudomotor/edema, and motor/trophic. To meet the criteria for CRPS, a patient must exhibit symptoms in at least two of these categories, along with the presence of ongoing pain disproportionate to the inciting event.
Diagnostic Criteria In Detail
The Budapest Criteria provide specific criteria for each of the four diagnostic categories, which are as follows:
- Sensory: Allodynia (pain caused by a stimulus that should not be painful) or hyperalgesia (increased sensitivity to pain)
- Vasomotor: Temperature asymmetry (temperature difference between the affected and unaffected limb), skin color changes, or skin color asymmetry
- Sudomotor/edema: Edema (swelling) or sweating changes (either increased or decreased sweating) in the affected limb
- Motor/trophic: Decreased range of motion, motor dysfunction (weakness, tremor, or dystonia), or trophic changes (hair, nail, or skin changes)
To be diagnosed with CRPS according to the Budapest Criteria, a patient must meet at least two of the four diagnostic categories, along with the presence of ongoing pain that is disproportionate to the inciting event or injury.
Case studies and real-life examples can help illustrate how the Budapest Criteria are applied in practice. For instance, a patient who experiences severe pain, swelling, and temperature changes in their hand after a minor injury may meet the criteria for CRPS if they also exhibit motor dysfunction or trophic changes, such as nail or skin changes in the affected limb.
Challenges And Limitations
While the Budapest Criteria have greatly improved the diagnostic process for CRPS, there are still some challenges and limitations associated with their use.
One of the main challenges is the subjective nature of certain criteria, such as the assessment of allodynia or hyperalgesia. These sensory disturbances can be difficult to measure objectively, and their interpretation may vary among healthcare professionals.
Additionally, some of the criteria, such as trophic changes or motor dysfunction, may not be present in the early stages of CRPS, potentially leading to a delayed or missed diagnosis.
It is important to note that the Budapest Criteria should be applied by experienced healthcare professionals who have a thorough understanding of CRPS and its diagnostic nuances. Misinterpretation or incorrect application of the criteria can lead to misdiagnosis or underdiagnosis, which can have significant consequences for the patient’s treatment and management.
Conclusion
Early and accurate diagnosis of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is crucial for effective treatment and management of this debilitating condition. The Budapest Criteria have played a pivotal role in standardizing the diagnostic process for CRPS, providing a set of guidelines that healthcare professionals can follow to ensure consistent and accurate diagnoses.
By requiring the presence of symptoms in at least two of the four diagnostic categories (sensory, vasomotor, sudomotor/edema, and motor/trophic), along with ongoing pain disproportionate to the inciting event, the Budapest Criteria offer a comprehensive framework for identifying CRPS.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and limitations associated with the Budapest Criteria, such as the subjective nature of certain criteria and the potential for misinterpretation. Experienced healthcare professionals with a deep understanding of CRPS and the diagnostic process are crucial for the proper application of these guidelines.
FAQs
The Budapest Criteria is a set of diagnostic guidelines developed by a group of international experts to aid in the accurate diagnosis of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS).
The Budapest Criteria provide a standardized framework for diagnosing CRPS, ensuring consistent and accurate diagnosis of the condition across healthcare professionals. This is crucial for appropriate treatment and management of CRPS.
The four main diagnostic categories of the Budapest Criteria are sensory, vasomotor, sudomotor/edema, and motor/trophic.
To meet the diagnostic criteria for CRPS according to the Budapest Criteria, a patient must exhibit symptoms in at least two of the four diagnostic categories, along with the presence of ongoing pain disproportionate to the inciting event.
While the Budapest Criteria have improved the diagnostic process for CRPS, there are still some challenges and limitations associated with their use. These include the subjective nature of certain criteria, the potential for misinterpretation, and the possibility of delayed or missed diagnoses in the early stages of the condition.